Best Describes the Process of Facilitated Diffusion
The electric charge and pH helps in the diffusion across the membrane. B potential energy must be used immediately or it is lost.
Simple Diffusion And Passive Transport Article Khan Academy
Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient.

. Diffusion is one of the forms of substance transport between cells. Essential Amino Acids Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane Terms in this set 25 Which best describes the process of facilitated diffusion across a cell membrane. View Test Prep - chap 2 bio lab 2 answers from BIOL 121 at Springfield College.
Movement of a solute down its concentration gradient with the help of membrane proteins. Which of the following best describes the process of facilitated diffusion. What is a Facilitated Diffusion Example in Real Life.
The molecule is released on the other side of the membrane. Facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion in that facilitated diffusion _____. This facilitated diffusion process is used by larger molecules such as enzymes.
For any type of diffusion to occur there must be a concentration gradient or what is the same there must be an unequal distribution. It is a selective process ie the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. Passive movement of solutes across a membrane down their concentration gradients with the involvement of membrane proteins For what purpose s might a cell transport materials across its plasma membrane.
A process mediated by ATP synthase pumps protons against their concentration gradient C. 3 Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport in which ionsmolecules cross the semi permeable membrane because permeases present in the membrane facilitate the transport. It uses natural entropy to move molecules from higher concentration to a lower concentration until the concentration becomes equalized.
It however prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. Asked Feb 20 in Biology Microbiology by juneone. Diffusion is the process of spreading new ideas from culture to culture.
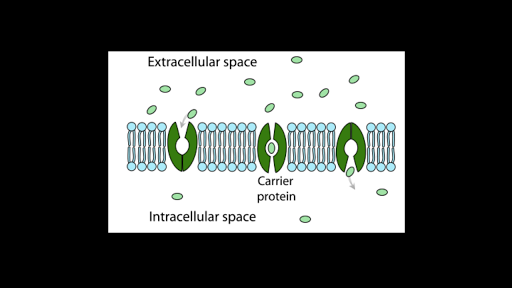
The carrier protein changes shape shielding the molecule from the interior of the membrane. There are five main types of. To import nutrients to get rid of wastes or to secrete proteins.
Like simple diffusion facilitated diffusion doesnt require metabolic energy and simply occurs across the concentration gradient. Answered Feb 20 by myia1988. Distinguish between monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Which of the following best describes the process of facilitated diffusion. Which of the following technological innovations facilitated indian ocean commerce. Facilitated diffusion of protons down an electrochemical gradient releases energy that is used in the synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pl Facilitated diffusion of protons down an.
Diffusion is the process by which particles tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. A signal protein d. Therefore diffusion is considered a type of.
There are plenty of examples of facilitated diffusion in the real world and in fact facilitated diffusion occurs probably every second in your body it is just that you cannot notice them. Energy is not required because the particles move along the concentration gradient. Facilitated diffusion is the process in which molecules pass across the.
Facilitated Diffusion Process Solutes moving through solution or a gas move randomly along a concentration gradient until there are equal numbers of particles in the two areas. Facilitated diffusion Which organelles are involved in the process called endocytosis vesicles Which process is occurring when a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases it contents outside the cell exocytosis describe what is shown if figure 33. Which of the following best describes the process of facilitated diffusion.
The diffusion facilitated is a type of passive cellular transport in which for the molecules to move inside the cellular solution it is necessary the intervention of some source of energy. The particles in the. Give examples of each.
Examples of diffusion include the use of cars and the smelting of iron. D kinetic energy is energy of motion. Simple diffusion facilitated diffusion active transport or secondary active transport Use the book to complete this tableChemical Digestion Absorption Enzyme Name Where is it Where.
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are two types of passive transport methods in which the cell membrane transports molecules across it. Main Difference Simple Diffusion vs Facilitated Diffusion. Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration with the help of a transport molecule.
Which term best describes the structure that is necessary for facilitated diffusion. Diffusion does not require the cell to expend atp. A Receptor-mediated endocytosis B Phagocytosis C Pinocytosis D Exocytosis E Co-transport.
A receptor protein b. Facilitated diffusion is the process of transporting particles into and out of a cell membrane. Since substances move along the direction of their concentration gradient chemical energy is not directly required.
The carrier protein then returns to its original shape. E water stored behind a dam is an example of kinetic energy. A energy in the chemical bonds of a molecule is kinetic energy.
A Osmosis B Diffusion C Facilitated diffusion D Active transport E None of the above 27 Which of the following best describes the transport process occurring in the diagram above. Facilitated diffusion also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport is the process of spontaneous passive transport as opposed to active transport of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. A molecule bonds to a carrier.
What process best describes the SGLT. C light energy is a form of chemical energy. What are the three main steps of facilitated diffusion.
The process by which NADH produced in glycolysis is transported into the mitochondrion b. In the human body particles and ions that cannot cross the cell membrane use carrier proteins to get into and out of the cell.
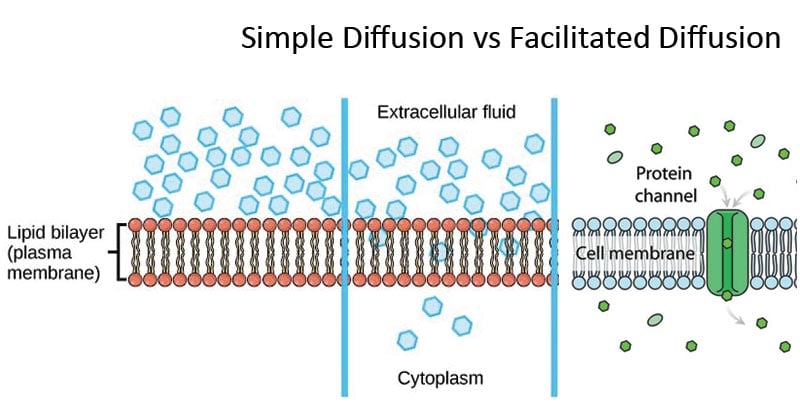
Simple Diffusion Vs Facilitated Diffusion 11 Differences

Honors Biology Lawrenceville Cells Plasma Membrane Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet

Facilitated Diffusion Definition Examples Quiz Biology Dictionary
No comments for "Best Describes the Process of Facilitated Diffusion"
Post a Comment